When a migraine hits, speed and safety both matter. You don’t just want relief-you want it without chest tightness, dizziness so bad you can’t drive, or a reaction that leaves you worse off than before. Three main classes of acute migraine meds exist today: triptans, gepants, and ditans. Each works differently, and their safety profiles aren’t interchangeable. Choosing the wrong one can mean days lost to side effects instead of recovery.
Triptans: Fast but Not for Everyone
Triptans like sumatriptan, rizatriptan, and almotriptan have been the go-to for over 30 years. They work by narrowing blood vessels around the brain and blocking pain signals. That’s why they often bring relief in under 30 minutes. But that same mechanism is also their biggest risk.
Triptans activate 5-HT1B receptors, which cause blood vessel constriction. That’s fine for most people-but dangerous if you have heart disease, uncontrolled high blood pressure, a history of stroke, or peripheral artery disease. The American Academy of Family Physicians clearly states: avoid triptans entirely if you have cardiovascular risk factors.
Even if you’re healthy, side effects are common. About 8-15% of users feel tingling or numbness. Around 5-12% get flushing or warmth in the face or chest. Up to 8% report a heavy, squeezing feeling in the chest-so intense that many mistake it for a heart attack. One Reddit user wrote: "Experienced severe chest pressure with first dose of Imitrex-never using it again." That reaction isn’t rare. In clinical trials, 3-8% of patients reported this sensation, and many stop taking triptans because of it.
Other frequent complaints: dizziness (7-14%), fatigue (5-9%), and drowsiness (6-10%). Subcutaneous injections cause injection-site pain in 40% of users. Nasal sprays leave a bitter aftertaste for about a quarter of people. The good news? Serious heart events like heart attacks are extremely rare in people without pre-existing conditions. A 2016 meta-analysis found no significant increase in serious adverse effects overall. But the discomfort? That’s real-and it’s why nearly 60% of users eventually quit triptans.
Gepants: The Safer Alternative for High-Risk Patients
Gepants like ubrogepant (Ubrelvy) and rimegepant (Nurtec ODT) work completely differently. Instead of constricting blood vessels, they block CGRP-a molecule that triggers migraine pain and inflammation. This means no cardiovascular risk. That’s why the American Headache Society now recommends gepants as a first choice for people with heart disease or stroke history.
The side effect profile is much gentler. Nausea affects only 4-6% of users. Drowsiness? Around 2-4%. Hypersensitivity reactions are rare-just 0.1% with rimegepant. No chest tightness. No tingling. No dizziness that knocks you out. One user on Drugs.com said: "No chest pressure like with triptans, just takes longer to work." That’s the trade-off: slower onset. Triptans often work in 30 minutes. Gepants take 1-2 hours.
But here’s the catch: gepants last longer. Their half-lives are 5-12 hours, meaning they may prevent a migraine from coming back within 24-48 hours. That’s a big advantage over triptans, which wear off faster. Rimegepant also has an added benefit-it’s approved for both acute treatment and prevention, taken every other day.
One limitation: drug interactions. Rimegepant shouldn’t be taken with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors like ketoconazole or clarithromycin. These can spike drug levels in your blood. Always check your other meds with your doctor.
Ditans: Powerful But Paralyzing
Lasmiditan (Reyvow) is the only ditan available. It targets 5-HT1F receptors, which affect pain pathways without touching blood vessels. So, no heart risks. That sounds perfect-until you feel the side effects.
In clinical trials, 18.8% of people taking lasmiditan 100mg reported dizziness. Compare that to 8.5% on placebo. Paresthesia (tingling or numbness) hit 9.4%. Sedation? 7.8%. Vertigo? 5.6%. Incoordination? 3.2%. These aren’t minor. They’re enough to make driving, working, or even walking safely impossible.
The FDA requires a black box warning: do not drive or operate machinery for at least 8 hours after taking Reyvow. A 2021 study confirmed driving impairment lasted up to 5 hours post-dose. Users on Reddit describe it as "feeling drunk without alcohol." One wrote: "Felt completely out of it for 6 hours after taking Reyvow-can’t function at work." That’s why it has the lowest user rating of the three: 5.8/10 on Drugs.com, with 63% of negative reviews citing sedation or dizziness.
Doctors avoid prescribing it unless other options fail. Dr. Rami Burstein from Harvard calls it unsuitable as a first-line treatment for people who need to return to daily tasks quickly. It’s also not recommended if you have a seizure history or take other drugs that lower the seizure threshold-even though actual seizure cases are rare.
Real-World Safety: Numbers Don’t Lie
A 2021 analysis of 64 trials involving over 46,000 people found clear safety rankings:
- Ditans had the highest risk of any adverse event-nearly 3 times more likely than placebo (OR 2.87).
- Triptans came next-moderately higher risk than placebo.
- Gepants had the lowest risk of all-closest to placebo.
When directly compared, triptans were 43% more likely to cause side effects than rimegepant and 38% more likely than ubrogepant. But here’s what’s surprising: triptans still worked better at reducing pain at the 2-hour mark. Gepants and ditans were slower. So if speed is your priority and you’re healthy, triptans still win. If safety is your priority, gepants lead.
Prescription data backs this up. In Q3 2023, triptans still made up 62% of acute migraine prescriptions. But gepants are surging-from 2% in 2020 to 28% today. Ditans? Just 3%. Why? Because patients and doctors are voting with their prescriptions. They’re choosing safety over speed when they can.
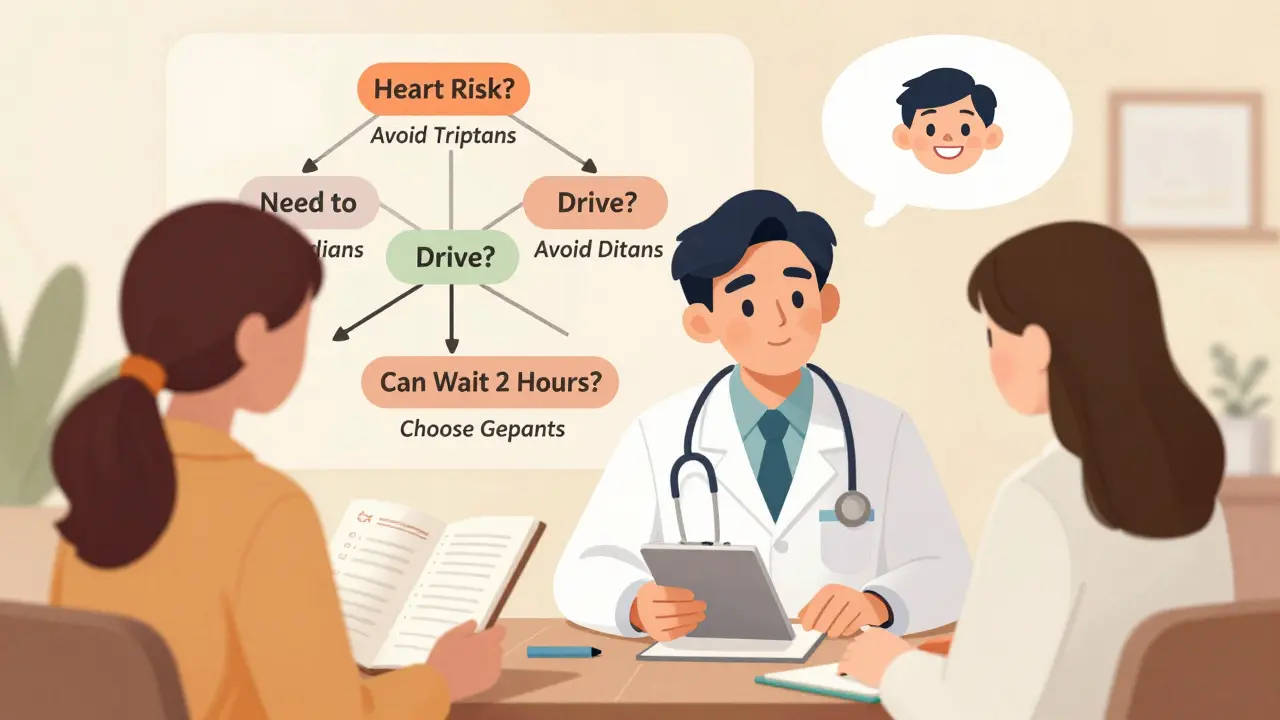
What to Do Next
If you’re on triptans and feel chest pressure, dizziness, or fatigue every time-you’re not imagining it. Talk to your doctor. Ask if a gepant might be safer for you.
If you’ve tried a ditan and felt "drugged," don’t blame yourself. It’s not weakness-it’s the drug’s design. There are better options.
Here’s what to ask your provider:
- Do I have any cardiovascular risk factors? If yes, skip triptans.
- Do I need to drive, work, or care for kids after taking my med? If yes, avoid ditans.
- Can I wait 1-2 hours for relief? If yes, gepants are the safest long-term choice.
- Have I tried more than one triptan? If not, you might just need a different one-almotriptan and frovatriptan have fewer side effects.
Also, remember: some symptoms you think are side effects might actually be part of your migraine. Fatigue, nausea, and brain fog are migraine symptoms too. A good doctor will help you sort out what’s the drug and what’s the attack.
Final Thoughts
There’s no single "best" migraine medication. The right one depends on your body, your life, and your risks. Triptans are fast but risky for some. Gepants are slow but safe. Ditans are powerful but paralyzing. Your goal isn’t to find the strongest drug-it’s to find the one that gets you back to your life without adding new problems.
For most people without heart disease, gepants are now the smartest first choice. For those who need fast relief and have no cardiovascular risks, triptans still hold value. Ditans? They’re a backup-reserved for when everything else fails.
The science is clear. The data is out there. Now it’s time to match the right tool to your life.
Are gepants safer than triptans for people with heart problems?
Yes. Gepants do not constrict blood vessels, so they’re safe for people with heart disease, high blood pressure, or stroke history. Triptans are contraindicated in these cases because they can trigger heart attacks or strokes by narrowing arteries. The American Headache Society recommends gepants as a preferred option for patients with cardiovascular risks.
Can I take ditans if I have anxiety or depression?
Ditans like lasmiditan can cause dizziness, sedation, and cognitive changes-even in people without mental health conditions. If you already struggle with brain fog, fatigue, or low energy from anxiety or depression, ditans may make those symptoms worse. Most doctors avoid prescribing them in these cases unless absolutely necessary. Gepants are a much better option.
How long do side effects from triptans last?
Most triptan side effects-like tingling, flushing, or dizziness-last 1-2 hours and fade as the drug leaves your system. Chest tightness usually resolves within 30-60 minutes. If symptoms persist beyond 2 hours or worsen, seek medical attention. Some people mistake lingering migraine symptoms for drug side effects, so tracking your symptoms with a journal helps clarify the cause.
Why are gepants so expensive?
Gepants are newer drugs, still under patent protection, which keeps prices high. A single dose can cost $70-$100 without insurance. However, many manufacturers offer savings cards that reduce out-of-pocket costs to under $10 per dose. Some insurance plans now cover them as preferred options due to their safety profile. Check with your pharmacy or the drugmaker’s patient assistance program.
Can I switch from triptans to gepants safely?
Yes. There’s no washout period needed. You can stop triptans and start a gepant the next time you have a migraine. No drug interactions exist between them. Many patients switch because they’re tired of chest pressure or dizziness. If you’re concerned about slower relief, give gepants a few tries-they often work better than expected after the first few uses.
If you’re unsure which medication fits your life, keep a simple log: note the drug, time taken, time to relief, side effects, and how you felt afterward. Bring it to your doctor. You don’t have to settle for a migraine treatment that leaves you worse off.


swarnima singh
January 17, 2026 AT 05:01kanchan tiwari
January 19, 2026 AT 00:07Bobbi-Marie Nova
January 20, 2026 AT 03:05john Mccoskey
January 21, 2026 AT 05:56Riya Katyal
January 22, 2026 AT 16:07Nicholas Gabriel
January 23, 2026 AT 10:29Cheryl Griffith
January 24, 2026 AT 22:48Isabella Reid
January 25, 2026 AT 20:21Jody Fahrenkrug
January 26, 2026 AT 10:05Kasey Summerer
January 27, 2026 AT 07:19Ryan Hutchison
January 29, 2026 AT 02:14Joie Cregin
January 29, 2026 AT 21:38